U.S. Wheat Production to Fall to Lowest Level Since 2002/03
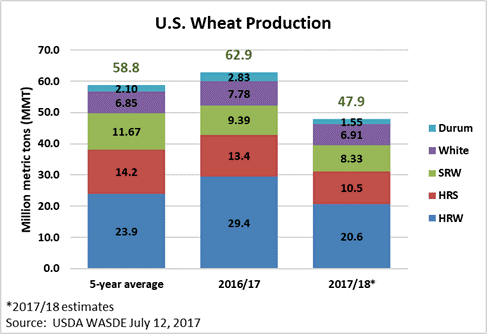
USDA forecast U.S. 2017/18 wheat production at 47.9 million metric tons (MMT), down 24 percent year over year and 18 percent below the 5-year average. The reason: an anticipated 12 percent decline in average yield and the lowest planted acres since USDA records began in 1919. However, USDA expects 2017/18 U.S. beginning stocks to total 32.2 MMT, up 21 percent year over year and the most since 1988/89. As a result, total 2017/18 U.S. wheat supply is forecast at 80.1 MMT, down 10 percent from 2016/17 but still 1 percent above the 5-year average of 79.3 MMT. USDA expects average yield to be 46.2 bu/acre (3.10 MT/ha), which is close to the 5-year average of 46.6 bu/acre (3.13 MT/ha).
On June 30, USDA estimated total planted wheat area would fall 9 percent year over year to 45.7 million acres (18.5 million hectares). If realized, that would be 17 percent lower than the 5-year average. USDA expects 2017/18 harvested area to drop 13 percent from last year and 18 percent below the 5-year average to 38.1 million acres (15.4 million hectares).
USDA forecast 2017/18 hard red winter (HRW) production to total 20.6 MMT, down 30 percent from 2016/17 and 14 percent below the 5-year average. A smaller planted area and sharply lower harvested area led to the decline. U.S. farmers planted 23.8 million acres (9.63 million hectares) of HRW for 2017/18, down 10 percent from 2016. Due to weather and wheat streak mosaic virus, harvested area in top HRW-producers Texas, Oklahoma and Kansas is projected to fall 16 percent year over year. USDA forecast 2017/18 HRW beginning stocks at 16.1 MMT, up 33 percent year over year and 81 percent above the 5-year average. Total 2017/18 HRW supply is expected to total 36.8 MMT, down 12 percent from 2016/17.
Soft red winter (SRW) production is also expected to decline 11 percent to 8.33 MMT in 2017/18 due to fewer planted acres. USDA estimated total 2017/18 SRW area at 5.61 million acres (2.27 million hectares), 15 percent lower than 2016/17 and 30 percent below the 5-year average. In contrast to recent years, SRW harvest in the U.S. Southern Plains is progressing rapidly with good harvest conditions. On July 7, the USW Weekly Harvest report showed the average grade on 199 samples was U.S. #2 in a generally sound crop with DON levels that are significantly below the 5-year average. USDA estimates that SRW 2017/18 beginning stocks totaled 5.85 MMT, up 37 percent from 2016/17 and 47 percent above the 5-year average. The larger beginning stocks will offset reduced production, and total 2017/18 SRW supply is expected to increase by 500,000 MT year over year to 14.2 MMT.
USDA reported white wheat production will decrease 11 percent from 2016/17 to 6.91 MMT, but still 1 percent above the 5-year average, if realized. The decline is due to 3 percent fewer planted acres and slightly lower forecast yields. Idaho, Oregon and Washington have received ample moisture and winter wheat conditions there average 78 percent good to excellent. USDA estimates soft white (SW) beginning stocks increased 42 percent year over year to 2.86 MMT. The larger beginning stocks are expected to offset the lower production, leaving the 2017/18 SW supply unchanged year over year at 9.77 MMT.
Hard red spring (HRS) production is expected to plummet in 2017/18 to 10.5 MMT, down 22 percent from the prior year and the lowest since 2002/03, if realized. The average spring wheat yield is forecast at 40.3 bu/acre (2.73 MT/ha), down 15 percent from 2016/17. USDA also estimates farmers planted 10.3 million acres (4.17 million hectares) to HRS, 10 percent below 2016/17 levels. As of July 11, 55 percent of North Dakota is in a severe or extreme drought and the remainder of the state is abnormally dry or in a moderate drought. Similarly, 72 percent of South Dakota and 45 percent of Montana are in a moderate to extreme drought. As of July 10, just 35 percent of the spring crop was rated good or excellent and 39 percent was poor or very poor. In North Dakota, the largest HRS producing state, 36 percent of the crop is in good or excellent condition. USDA anticipates 2017/18 HRS beginning stocks of 6.39 MMT are 14 percent less than last year. Estimated 2017/18 HRS supply will total 16.9 MMT, down 19 percent year over year. USDA expects the HRS stocks-to-use ratio to fall to 22 percent in 2017/18, compared to 41 percent one year prior.
Smaller planted area and 30 percent lower yields are expected to reduce durum production to 1.55 MMT in 2017/18, down an estimated 45 percent from 2016/17 and 26 percent below the 5-year average. USDA expects average durum yields to sink to 30.9 bu/acre (2.08 MT/ha), compared to 44.0 bu/acre (2.96 bu/acre) in 2016/17. Durum planted area decreased this year as farmers responded to lower prices and large carry-out stocks. Spring-planted northern durum is grown primarily in North Dakota and Montana, and the Desert Durum® harvest in Arizona and California is nearly complete. USDA estimates 2017/18 durum beginning stocks at 980,000 MT, up 29 percent from the prior year and 45 percent greater than the 5-year average. Increased beginning stocks will not offset the drastically reduced 2017/18 production so USDA expects the U.S. durum supply will fall to 2.53 MMT, 29 percent below 2016/17 levels and 9 percent below the 5-year average. The U.S. durum stocks-to-use ratio will fall to 24 percent, on par with the 5-year average.
Even with reduced production for 2017/18, U.S. farmers stored significant amounts of grain last year, ensuring that customers can continue purchasing reliable, high-quality wheat. Customers are encouraged to contact their local USW representative to discuss purchasing strategies in this volatile global wheat market.