Secondary Rail Rates, Tight Elevation Capacity Continue to Support Wheat Export Prices
By Claire Hutchins, U.S. Wheat Associates Market Analyst
Gulf and Pacific Northwest (PNW) hard red spring (HRS) and hard red winter (HRW) basis values have jumped significantly in the last month due to increased domestic secondary rail rates and limited export elevation capacity, both driven by stronger-than-expected U.S. agricultural export sales to China.
It is important for overseas wheat buyers to understand the potentially significant impact of price movement in the domestic secondary rail market on export prices.
U.S. railroads auction domestic freight in the “primary railcar auction market.” Grain shippers can meet their need for rail capacity by trading this freight among themselves in the secondary railcar auction market at prices above or below the primary tariff rate, depending on national supply and demand conditions. According to the USDA Agricultural Marketing Service (AMS), the secondary railcar market evolved to enable rail movements of grain to be more responsive to market pressures, like increased commodity exports or reduced railcar availability.
This year, AMS data show the average secondary rate for shuttle trains to be delivered in October was up 36 percent between July 30 and Aug. 20 to $1,172/car, nearly three times greater than the previous 3-year average.
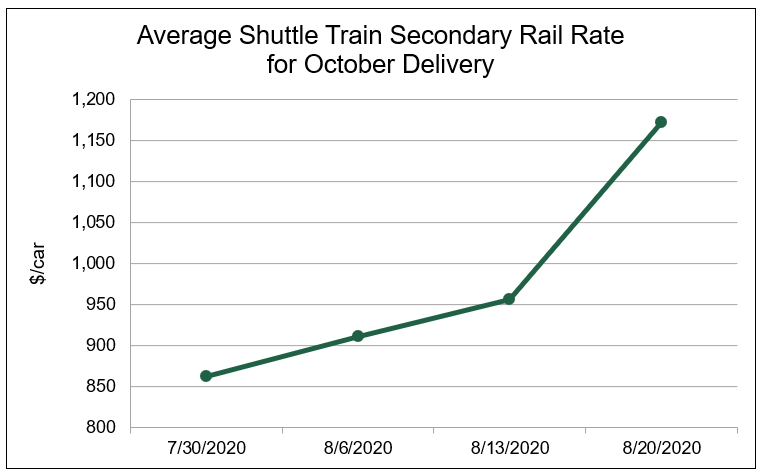
Source: USDA AMS Grain Transportation Report data
Over the same period, Gulf HRS 14.0 (12% moisture basis) export basis increased 16 percent to $2.20/bu, PNW HRS 14.0 export basis increased 21 percent to $2.00/bu. Gulf HRW 12.0 export basis increased 11 percent to $1.95/bu and PNW HRW 12.0 increased 24 percent to $2.55/bu.
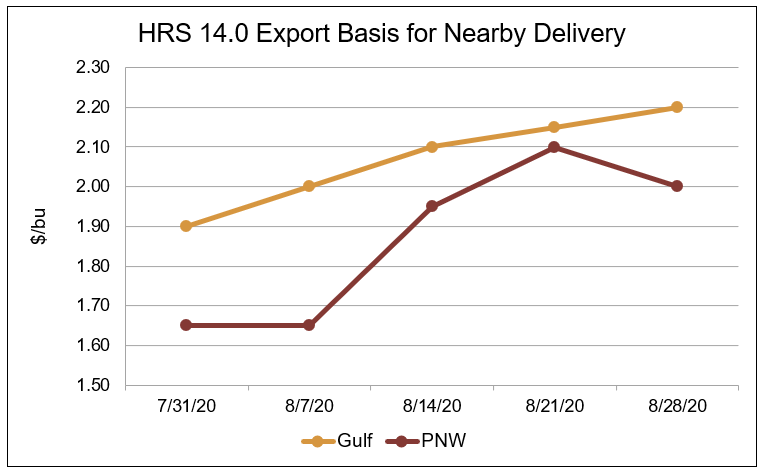
Source: U.S. Wheat Associates Price Report data
According to U.S. grain traders, the unexpectedly swift pace of agricultural commodity exports to China and rail labor shortages due to COVID-19 furloughs are supporting secondary rates and, in turn, wheat export basis levels.
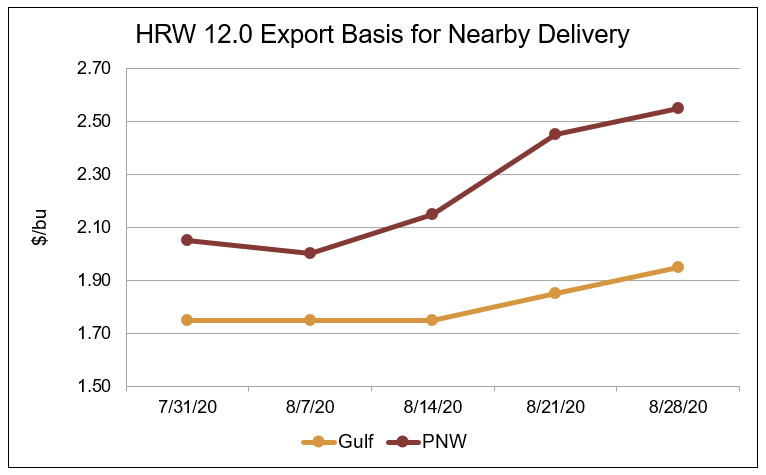
Source: U.S. Wheat Associates Price Report data
“If rail logistics through October, November and December run smoothly, we could see secondary rail rates plateau,” said one grain trader. “But if things go wrong in terms of weather or continued labor shortages, we could see more upside to secondary rail rates in the near future.”
Limited export elevation capacity out of the Gulf and PNW due to the swift uptick in Chinese demand for U.S. agricultural goods continues to add support to wheat export basis values.
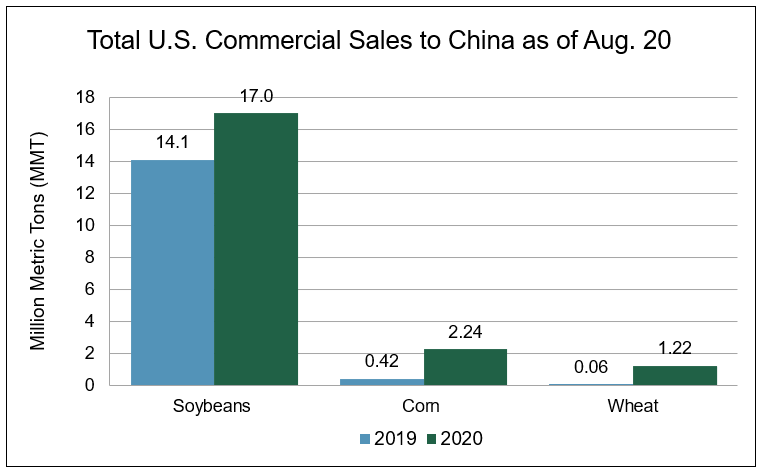
Source: USDA FAS export sales data
“September and October are at capacity; we can’t add a lot more business for those months. If anyone were to sell anything for delivery in those periods, it would raise elevation costs substantially,” said another grain trader. Additionally, export elevators are going to charge more to elevate wheat in the next couple of months because they expect to store more corn and beans at that time of year. It is more complex and expensive for export elevators to handle multiple commodities at the same time, said a representative from the U.S. grain trade.
Soybeans. “A lot of customers are surprised by the fact that export capacity is filling up so quickly with soybeans,” said a U.S. grain trader. The reason, however, is no surprise: China’s dramatic increase in U.S. soybean purchases this year compared to previous years. According to USDA, China bought 17.0 million metric tons (MMT) of U.S. soybeans for delivery in the soybean marketing year 2019/20, which ended Aug. 31. That is 21 percent more than the 14.1 MMT China purchased for delivery in marketing year 2018/19.
Corn. Export sales to China for marketing year 2019/20, at 2.24 MMT, are more than five times greater than the amount sold in 2018/19.
Wheat. It is no secret China has re-emerged as a buyer of U.S. wheat in a big way. According to USDA, as of Aug. 20, total U.S. wheat export sales to China total 1.22 MMT, for delivery in the current wheat marketing year. magnitudes greater than the 60,500 metric tons (MT) sold this time last year. China is currently the second largest market for U.S. wheat in marketing year 2020/21, which started June 1.
“If China wants to purchase more U.S. wheat for October, November and December deliveries, we could see export basis levels go higher in the near future,” said an industry contact.


