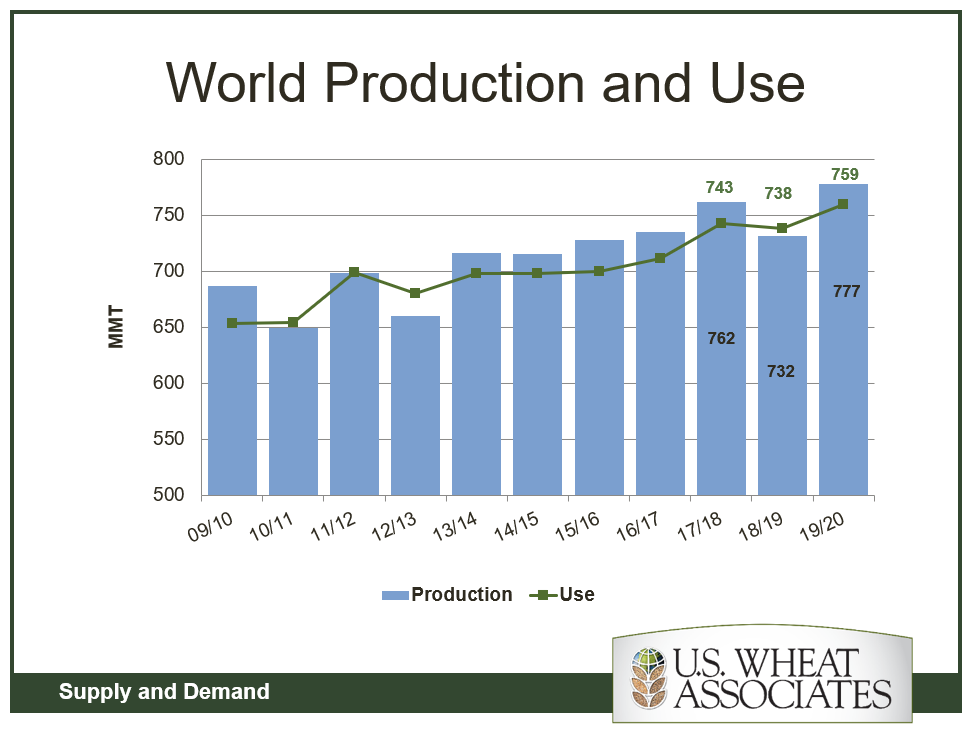
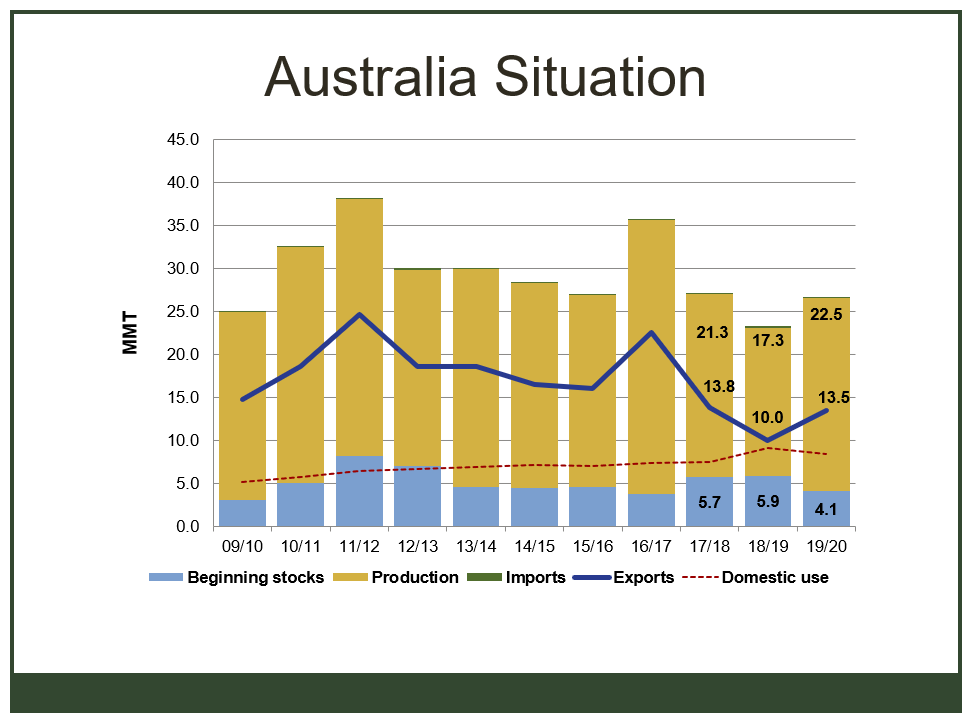
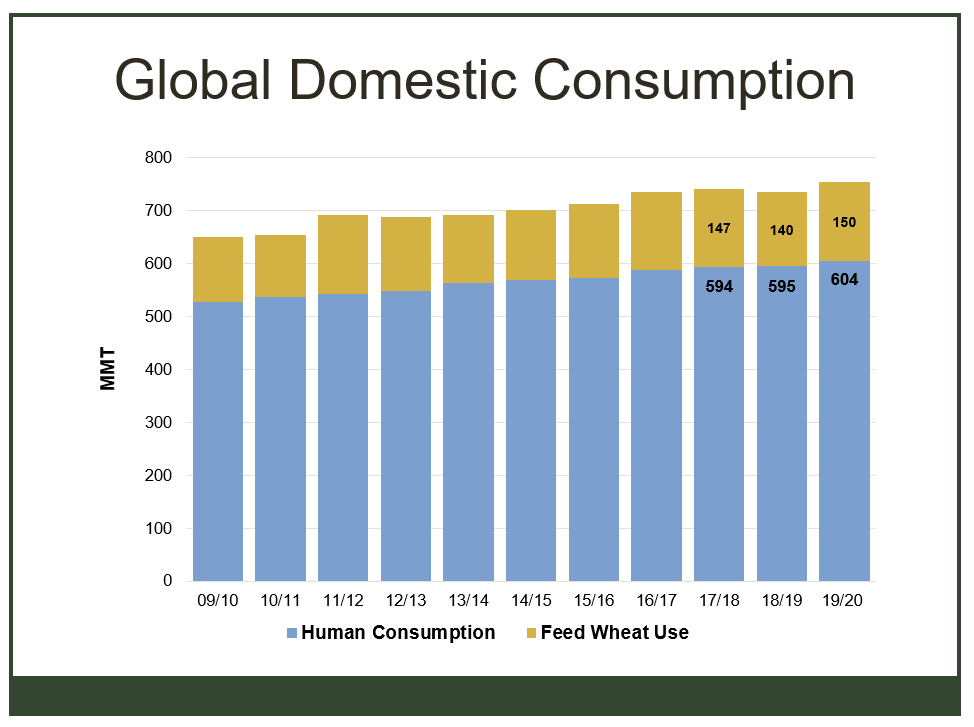
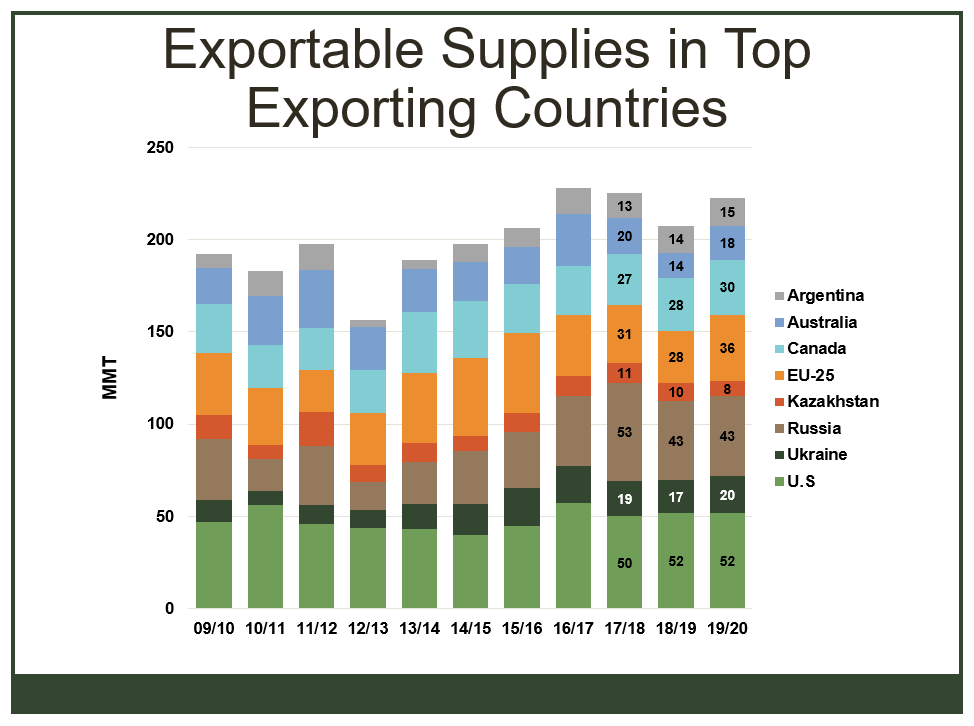
It is certainly true that the trade relations between the United States and China are in a difficult place. With the latest round of tariff increases announced and imposed, it is certainly possible to imagine that this conflict will not end soon. But we must all remember that negotiations are happening, and reworking the trading relationship between the two largest economies in history was never going to be easy.
In the meantime, U.S. Wheat Associates (USW) stands firmly by the following article by USW President Vince Peterson, “In Spite of Trade Conflicts, U.S. Wheat Farmers Will Not Abandon Customers in China,” published in “Wheat Letter” nine months ago.
USW remains engaged in keeping our once and future customers in China informed about the quality, variety and value of U.S. wheat in anticipation of future opportunities. Upcoming work includes a short course on contracting for wheat value, baking demonstrations in cooperation with the USDA’s Foreign Agricultural Service trade office in Beijing, and additional technical milling support activities in China. The commitment to service there will continue long after this trade conflict has ended.
In Spite of Trade Conflicts, U.S. Wheat Farmers Will Not Abandon Customers in China
By Vince Peterson, USW President. Originally published August 21, 2018.
Chinese Vice Minister of Agriculture Han Jun recently acknowledged the decades of work that U.S. farmers have put into growing the Chinese market for U.S agriculture. He then warned that this market may never come back to where it was if the trade dispute with the United States continues much longer.
We can guarantee the Vice Minister, and the wheat food industry in China, that U.S. Wheat Associates (USW) and the farmers we represent will not turn our backs on our outstanding customers in China. We remain dedicated to our core mission in China, as we are everywhere in the world, to bring profitability and value to our customers even if that is temporarily more difficult today.
Presumably, Chinese leaders believe that U.S. farmers can persuade the Trump Administration to end this trade war with China. However, U.S. farmers have been clear with their own government that China’s predictable response to the conflict has harmed them and we have supported negotiations to resolve this conflict. While we agree that escalating rounds of tariffs are a bad idea, we also believe that many of the U.S. government complaints about China’s policies are valid.
In our experience, state disruption of the wheat trade has been an enormous problem, severely limiting opportunities and profitability for both U.S. farmers and our wheat food industry customers in China. Through opaque administration of its wheat tariff rate quota (TRQ), China has deprived its flour mills of an average of 6.5 MMT of imported wheat annually over the past decade. In fact, recent import volumes are still well below what China imported in the 1980s and early 1990s; that is, before it joined the World Trade Organization (WTO). One could be forgiven for thinking China was a more promising market before joining the WTO than after; almost entirely because of excessive subsidies to the domestic wheat crop in recent years, as well as tight limits on TRQ access. This is why the U.S. government, under the Obama Administration, initiated two WTO cases on these issues in the fall of 2016. The prosecution of those cases has been continued and pressed forward by the Trump Administration. We are highly supportive of this action.
The Chinese government should recognize that its many years of flouting international commitments and highly interventionist “state capitalism” have led directly to the present conflict. If China had lived up to the commitments made when it joined the WTO, it is highly doubtful that we would still find ourselves in this situation. If Chinese leaders want to avoid further conflict and bolster the international trading system that they claim to defend, China can first start behaving like a responsible economy and adhere to its trade commitments in both letter and spirit. Of course, we are urging the same from the United States, which must also approach China with clear demands and a path towards achieving them.
Nevertheless, we are confident that this trade confrontation will one day be resolved. In the meantime, we will continue to reach out to our customers and friends in China, to reassure them of our unfailing dedication to our work with them. Further, we will make the guarantee that, once this trade dispute is resolved and behind us, we will work harder than ever to continue earning their business as we chart a path, together, to build the commercial channels that hold so much promise for Chinese and American industries and people.