For 40 years, U.S. wheat farmers have supported U.S. Wheat Associates’ (USW) efforts to work directly with buyers and promote their six classes of wheat. Their contributions to state wheat commissions, who in turn contribute a portion of those funds to USW, qualifies USW to apply for export market development funds managed by USDA’s Foreign Agricultural Service. Currently, 17 state wheat commissions are USW members and this series highlights those partnerships and the work being done state-by-state to provide unmatched service. Behind the world’s most reliable supply of wheat are the world’s most dependable people – and that includes our state wheat commissions.
Member: Texas Wheat Producers Board
Member of USW since 1980
Location: Amarillo, Tex.
Classes of wheat grown: Hard Red Winter (HRW) and Soft Red Winter (SRW)
The Texas Wheat Producers Board (TWPB) was established in 1971 to provide support and funding for wheat research, education and market development. The fifteen-person board, which operates on a two-cent-per-bushel checkoff fund, is committed to ensuring the competitiveness of Texas wheat in domestic and international markets. These goals are accomplished through unique partnerships with U.S. Wheat Associates, and Plains Grains, Inc. Current research shows that wheat growers receive a $23 dollar return for every dollar invested in overseas marketing efforts.
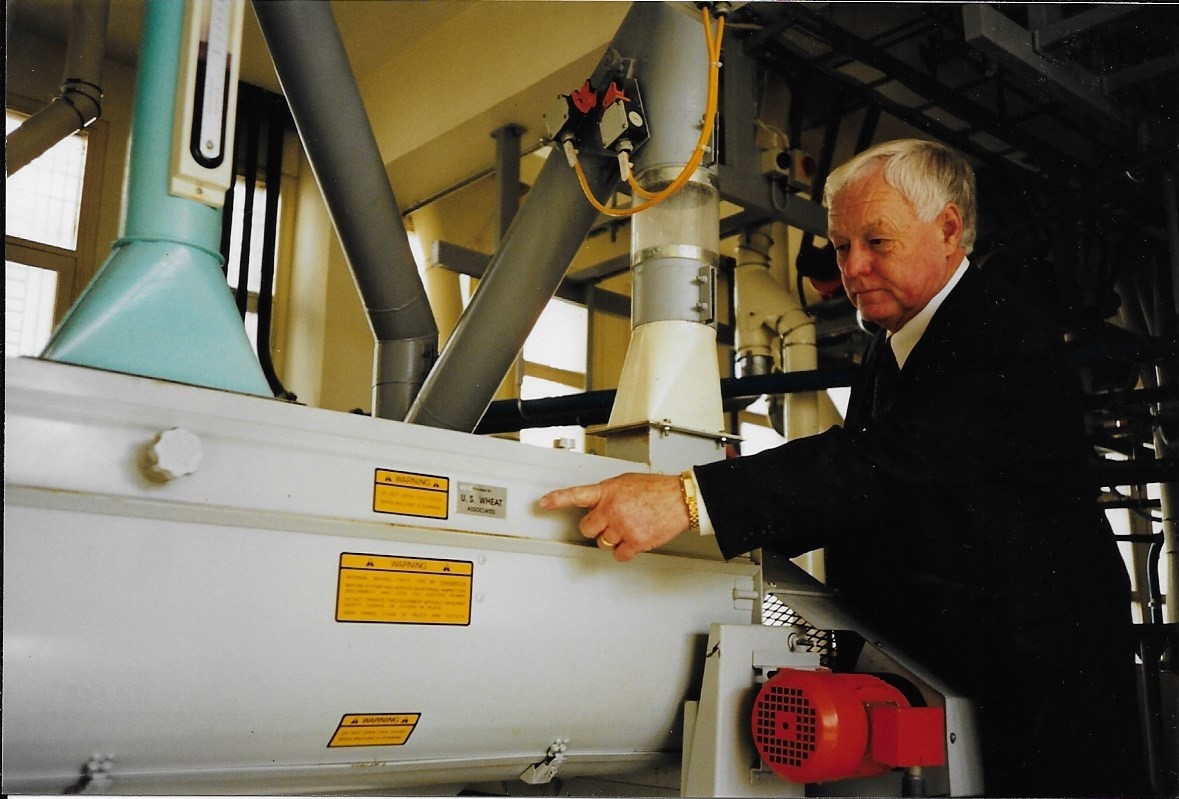

Jack Norman served on the Texas Wheat Producers Board for 30 years and attended many USW events in that time. In 1998, he traveled with USW to Morocco, Kenya and Egypt. Jack retired from the Texas Wheat board last year.
Why is export market development important to Texas wheat farmers and why do they continue to support USW and its activities?
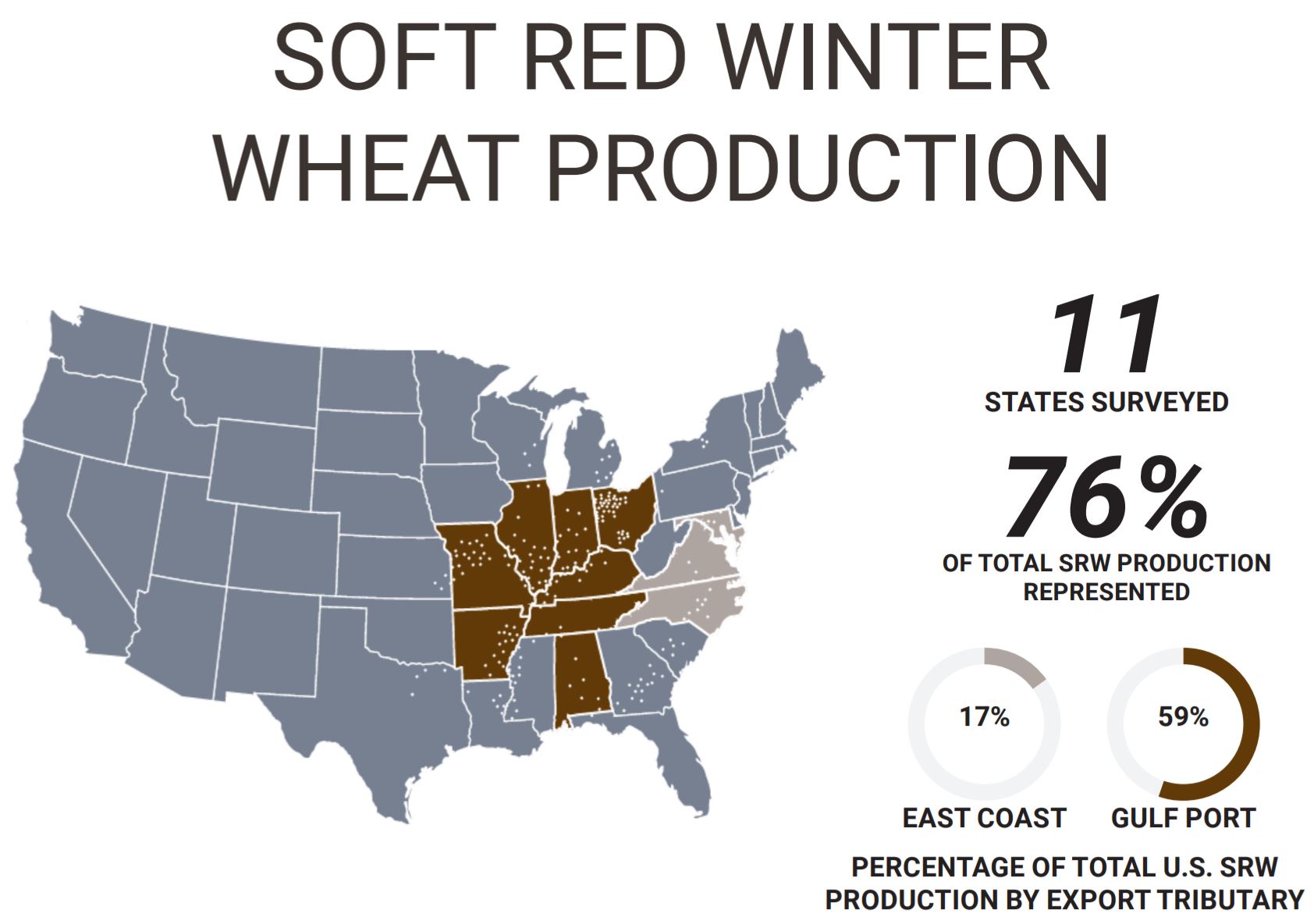
More than 50 percent of the wheat produced in Texas is exported every year. The TWPB has made it a priority to develop and maintain strong relationships with overseas customers to ensure the profitability of high-quality Texas HRW and SRW wheat. We are uniquely located geographically. The ports along the Texas coast, most prominently the Port of Houston, move over one-third of the wheat exported by the United States. Our location is highly accessible for Mexico, the largest importer of Texas wheat and consistently one of the top importers of U.S. wheat overall. It is imperative to our mission that we work with USW to promote wheat, expand market access and maintain good relationships with overseas customers. We believe the work done by USW will not only help us achieve our goals but also create a better future for all wheat producers.
How have Texas wheat farmers recently connected with overseas customers?
TWPB members have a long history of taking part in overseas trade mission trips, as well as hosting international trade delegations in Texas, and we value the experiences built through meeting customers face-to-face. Although the global pandemic put on hold on these meetings, we have used virtual platforms to connect with vital markets. In June, we joined USW for a virtual meeting with African wheat buyers, providing background on how wheat is produced in Texas and sharing updates on the 2020 wheat harvest. In July, our staff participated in another virtual meeting with Chilean flour milling executives and worked with Colorado Wheat staff to give an overview of 2020 HRW wheat quality. Both these virtual meetings gave us the opportunity to discuss the importance of Texas in the wheat production cycle, from the development of new varieties to the export of grain from our ports, which will help carry out our mission to increase demand of Texas-grown wheat.
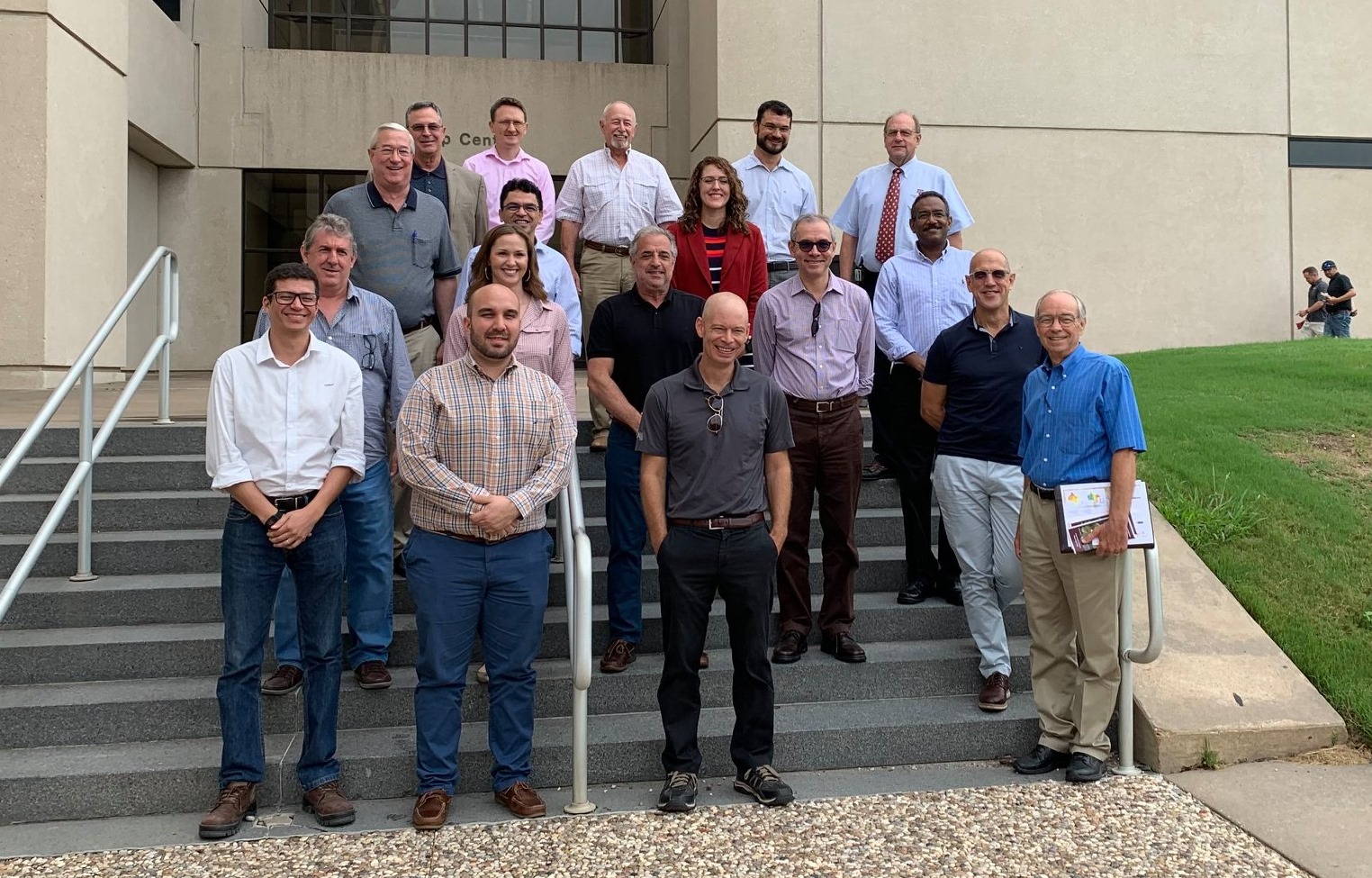

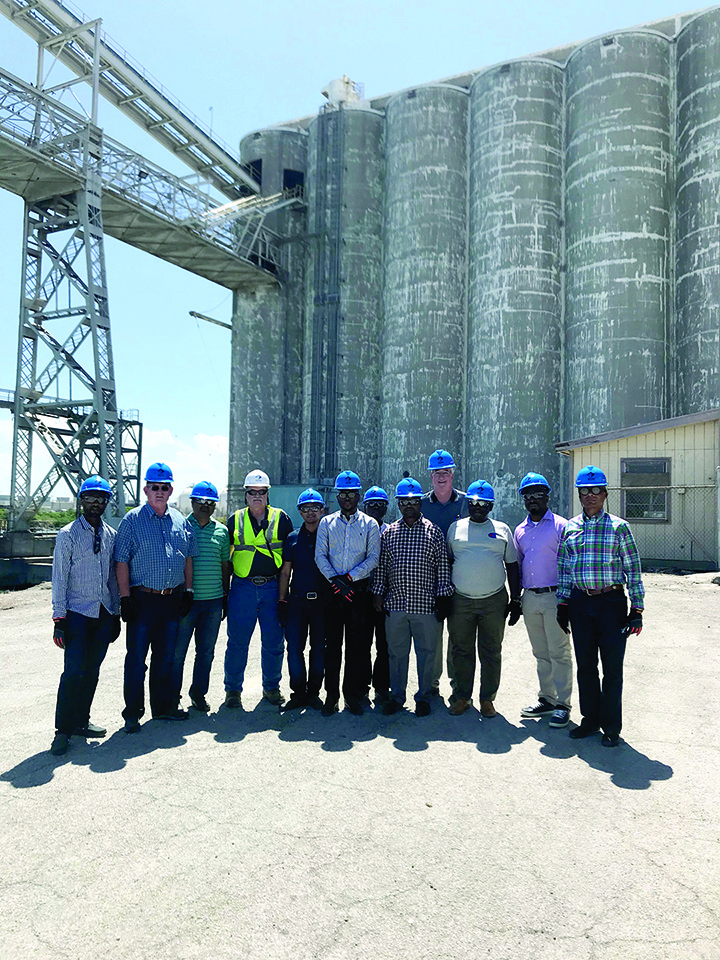
A USW Brazilian Trade Delegation in College Station, Texas, in 2019, after a tour of the Texas A&M wheat breeding and research labs.
What is happening lately in Texas that overseas customers should know about?
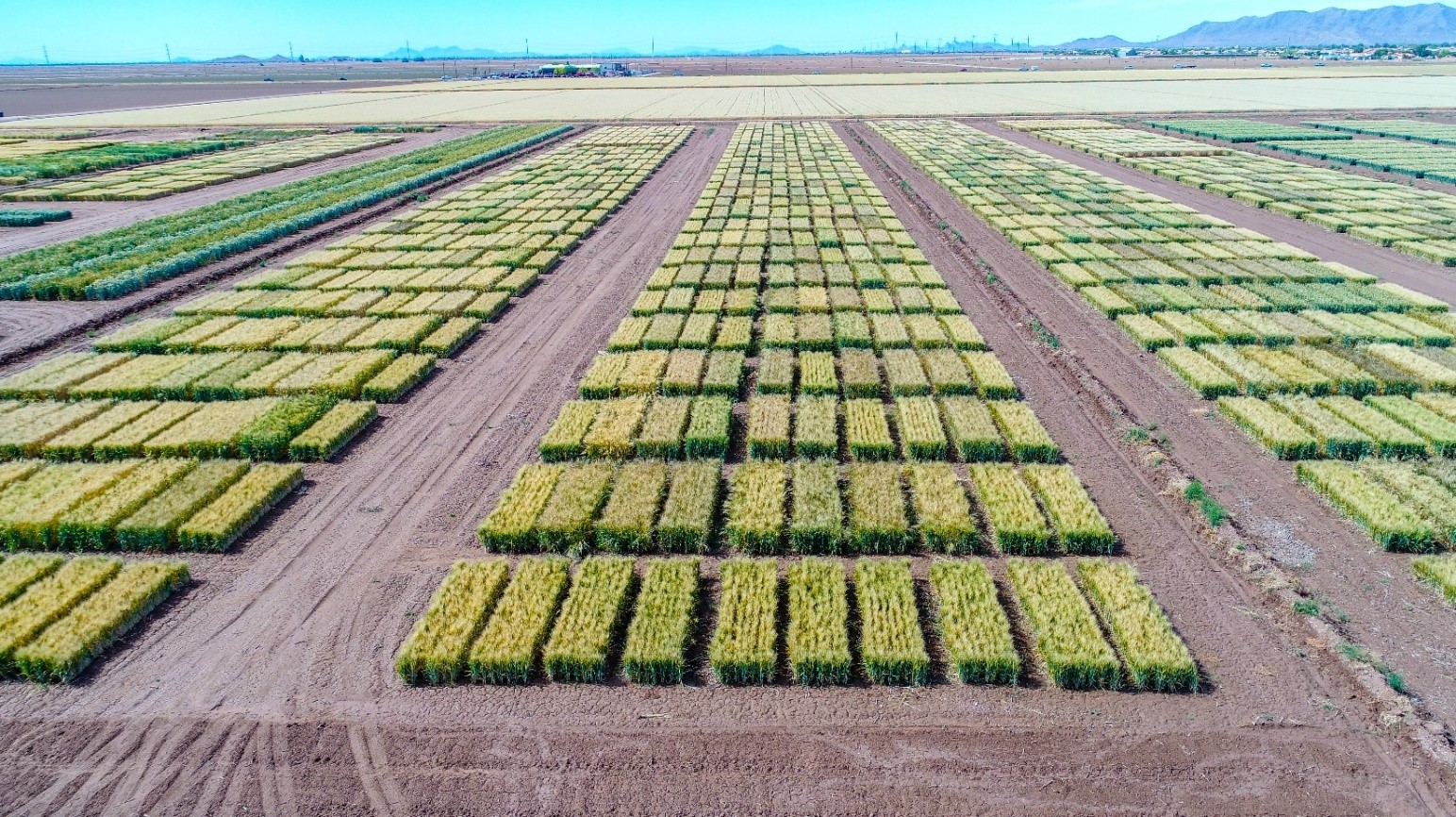
The TWPB has always put a major focus on research. Based on the feedback from overseas markets, we have invested in projects aimed at enhancing end-use quality in order to produce a product with more functionality for our customers. Last year, our state researchers released two new winter wheat varieties that performed well with fewer inputs, decreasing the financial burden on farmers, while demonstrating exceptional milling and baking characteristics. Because of this research, we can supply a high-quality wheat without impacting the cost.
The board has also been active in trade policy. We have actively engaged with U.S. government officials, including the Office of the United States Trade Representative (USTR), to promote expansion of trade access and avoid market disruption due to tariff implementation. It is our priority to provide overseas customers with a high-quality wheat that is also affordable, and we will continue to work with USW to promote favorable trade agreements.
Learn more about the Texas Wheat Producers Board on its website here and on Facebook and Twitter.
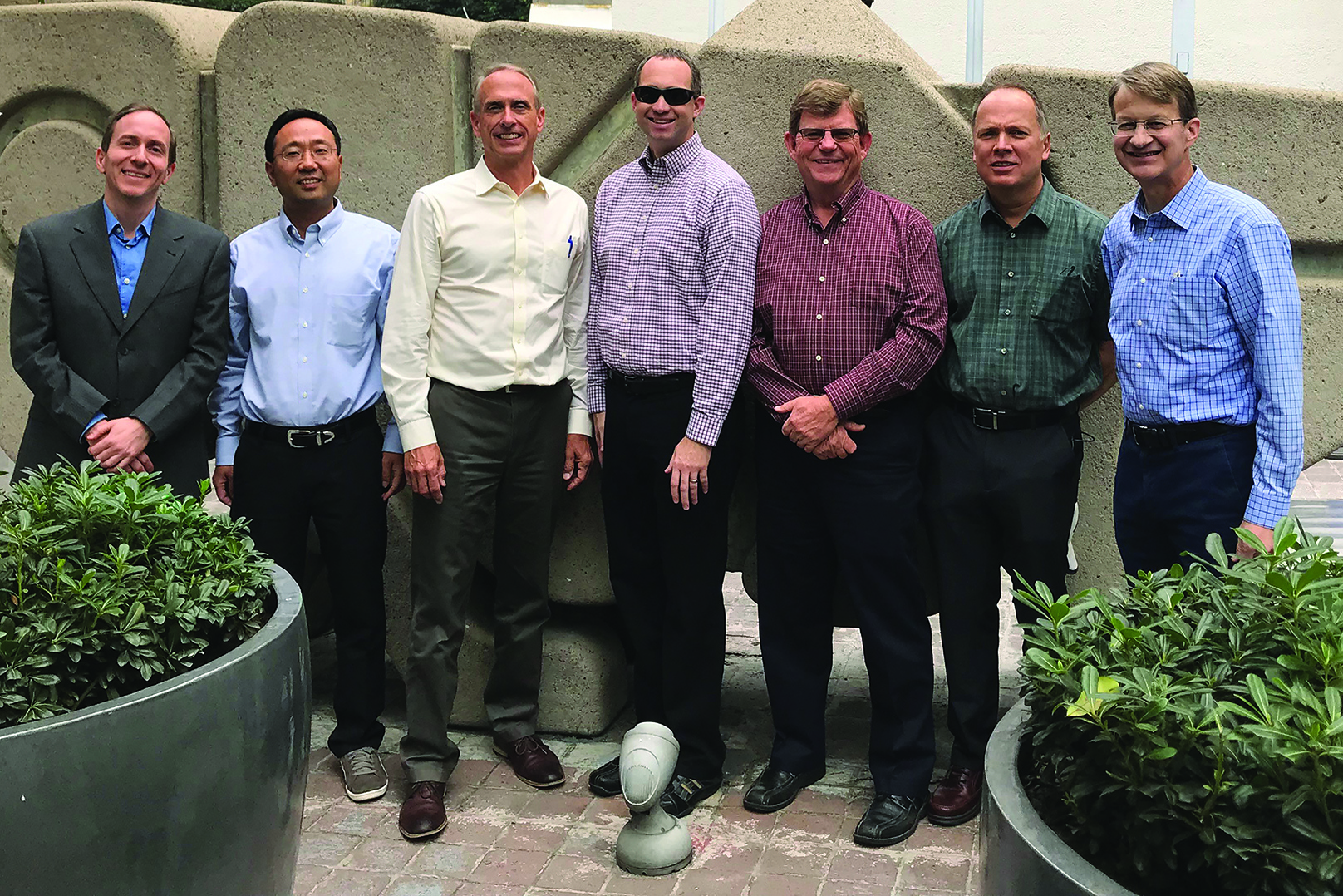

TWPB sponsored a Texas A&M AgriLife Research wheat breeder, Dr. Jackie Rudd, on his trip to the 2019 USW Breeders Team to Latin America. He attended in order to connect with buyers on their quality needs and he has implemented their feedback directly into the Texas breeding program.

In 2015, a delegation of Texas Wheat representatives, including current USW board member Ken Davis (middle), traveled to Cuba for a trade alliance meeting.