Global demand for wheat food grows stronger every year, making exports vitally important to U.S. wheat farmers. As the export market development organization for the U.S. wheat industry, U.S. Wheat Associates (USW) works to help wheat buyers, millers, bakers, wheat food processors and government officials understand the quality, value and reliability of all six U.S. wheat classes. USW relies on its successful working relationships with world-class educational partners that enhance its technical and trade service assistance to help separate U.S. wheat from its competitors. One of those partners is the Wheat Marketing Center (WMC) in Portland, Ore.
Located in the historic Albers Mill Building, WMC is a research and educational bridge between U.S. wheat farmers and their customers, dedicated to linking quality wheat and quality end products.
“Consumer tastes are evolving in domestic and international markets,” said Janice Cooper*, WMC Managing Director. “WMC’s programs demonstrate how U.S. wheat can be used to meet changing consumer demand with products that are nutritious and cost-competitive.”
In the mid-1980s, several state wheat commissions saw a need for a research and training facility to help U.S. wheat customers understand how to utilize U.S. wheat best. With the help of the late Oregon Senator Mark Hatfield – who helped secure a federal grant to renovate the Albers Mill Building – WMC opened in 1988. Its charter members, state wheat commissions from Oregon, Washington, Idaho, Montana, North Dakota, Colorado, Nebraska and the Port of Portland, and five additional industry members make up its board leadership. The building is also home to the Oregon Wheat Commission, Federal Grain Inspection Service, and the USW West Coast Office.

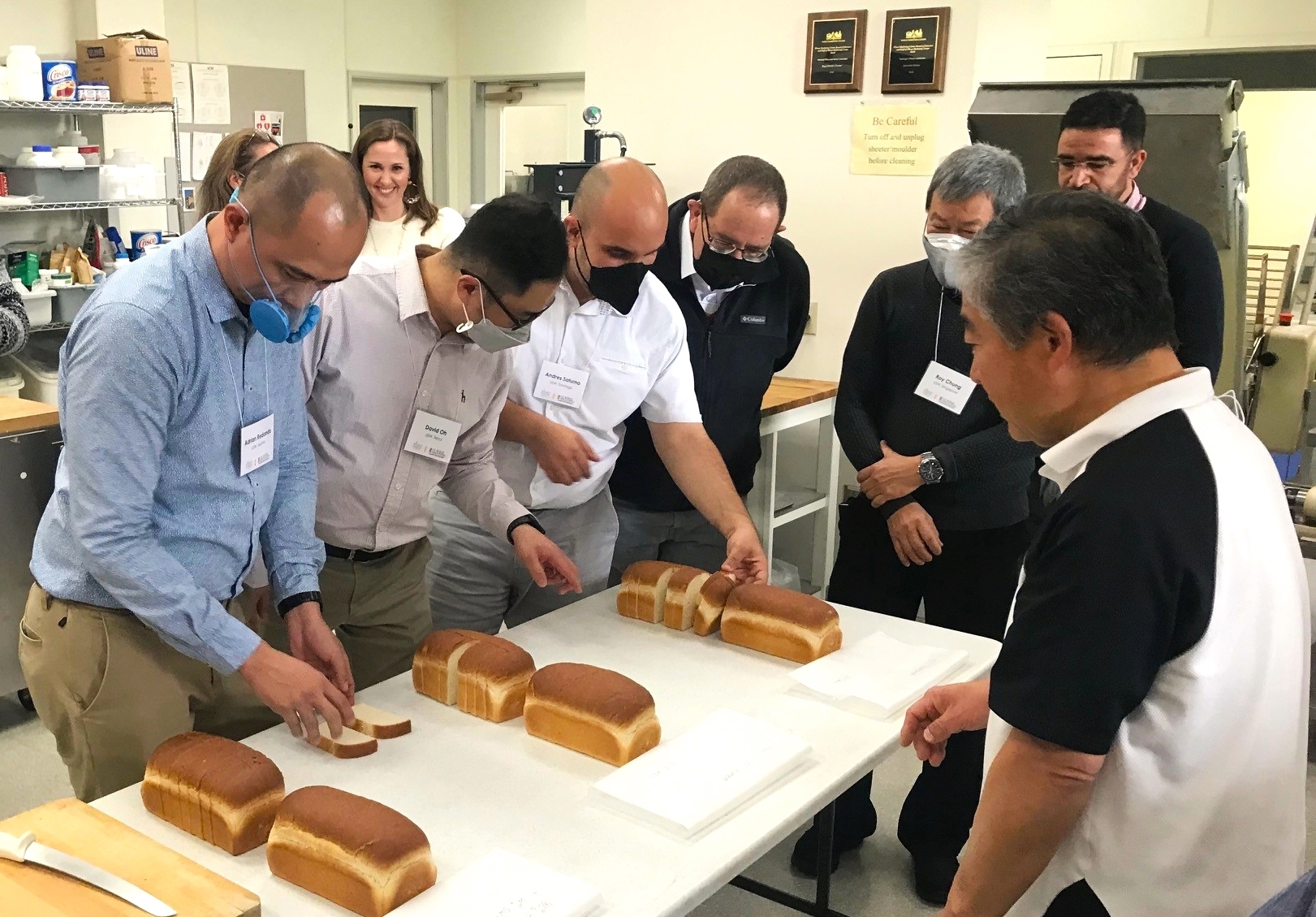
Technical Training. Dr. Jayne Bock, Wheat Marketing Center Technical Director, discusses baguette qualities with David Oh, USW Seoul; Adrian Redondo, USW Manila; and WMC Managing Director Janice Cooper in March during a core competency training session.
Three Pillars of Work
WMC programming focuses on three pillars: technical training, research and crop quality testing.
Every year, USW identifies U.S. wheat market needs and works in partnership with WMC to provide technical training courses focused on addressing those topics. In March, WMC welcomed USW technical staff from around the world to a dynamic course focusing on technical solutions to customer challenges. And USW has commissioned several new research projects from WMC related to rapid visco analysis (RVA), sponge cake methodology, U.S. wheat flour blending options and other studies that will benefit overseas customers.
WMC also hosts a variety of other technical training courses, including independent courses that it organizes itself, partnerships with other entities and custom proprietary company courses.
In addition to technical training, WMC is involved in innovative research and product development.
“We identify research projects based on market need and market opportunity,” said Cooper. “If there is a challenge with the wheat harvest, we identify what research can be done to help navigate U.S. wheat customers through those challenges. Likewise, we study market demand and look for opportunities to help the industry move in new directions with new products.”
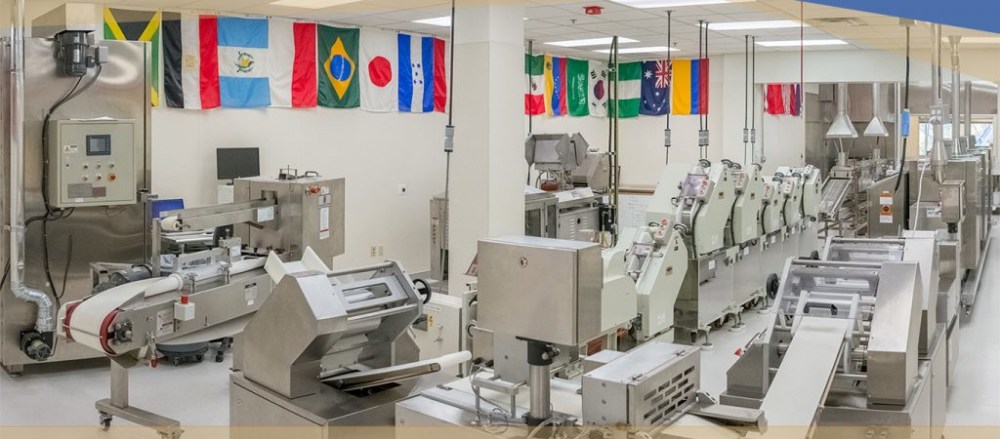
WMC uses its several pilot-scale lines to give participants a hands-on experience.
“From crackers to Asian noodles and cookies to a full baking lab, we have the ability to make a wide array of wheat products in-house,” said Cooper. “This equipment is the perfect size to link what is done in a research and development lab and a full-scale food production facility, which is ideal for research, training and product development.”
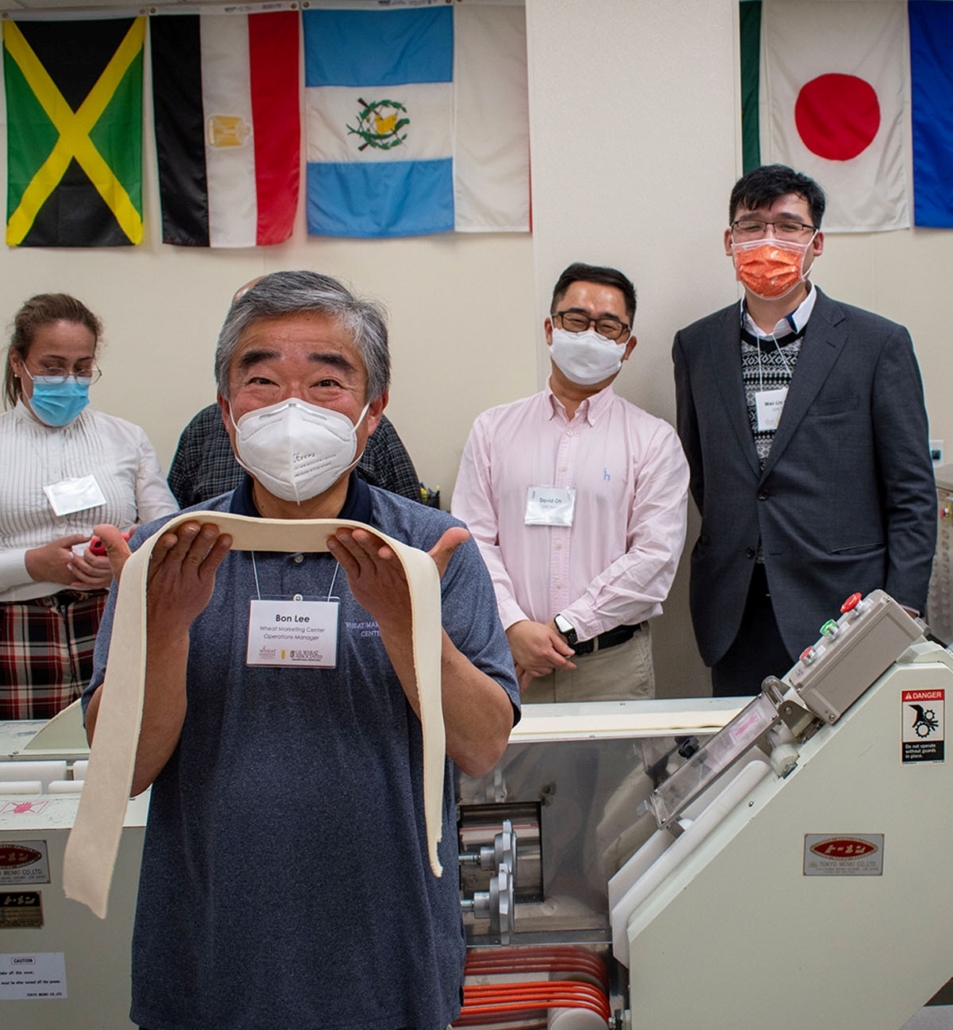

Noodle Line Ready. Bon Lee, Wheat Marketing Center Operations Manager, holds dough strips to be used in the educational partner’s pilot noodle line. In the background, Claudia Gomez, USW Santiago; David Oh, USW Seoul; and Wei-lin Chou, USW Taipei, were at the WMC with other USW technical colleagues in March for a training conference.
Testing the quality of the crop is also an important service WMC provides. Each year it tests the quality of the Pacific Northwest (PNW) harvest and makes those results available in weekly reports on its website, as well as in USW’s weekly harvest report. WMC is responsible for the soft white (SW) and hard white (HW) wheat analysis featured in the annual USW Crop Quality Report and an additional, more extensive SW regional report.
Customer Focus
While many of its programs are focused on U.S. wheat customers, it is also important for the WMC to share why striving for better wheat quality is important and at the root of its mission. Throughout the year, WMC hosts several grower workshops and programs for other visiting food and agriculture groups.
“The best way to explain what we do and why is for people to visit,” said Cooper. “With the other wheat industry partners in our building and our proximity to the many export elevators here, it makes visiting the Wheat Marketing Center a well-rounded opportunity.”
For those searching for more information instead of a visit, the WMC website serves as a gateway for valuable multi-media resources on research, the facility’s equipment, crop quality and testing. Ultimately, Cooper wants U.S. wheat farmers and customers to understand how WMC is helping the industry continue to move forward.
Building Knowledge
“We are unique because our focus is on end products, technology and giving customers a hands-on opportunity to take products made with a control flour that they are already using and compare it side by side with U.S. wheat and see the difference for themselves,” said Cooper. “Customers leave with a better appreciation of how valuable U.S. wheat really is and an understanding of the commitment made by U.S. wheat farmers to provide the flour they need to make the highest quality end products they are looking for.”
Learn more about the Wheat Marketing Center and its programming and services at https://www.wmcinc.org/.
*Cooper plans to retire from WMC in 2022, and the search for her successor is underway. Also, WMC has hired Ms. Liman Liu to train with Bon Lee. Liu has extensive commercial baking and product development experience, having spent the last eight years at Dave’s Killer Bread (now part of Flowers Foods.)
By Amanda J. Spoo, USW Director of Communications
Read about other USW educational partners in this series:
Northern Crops Institute Continues Tradition of Adding Value to U.S. Spring Wheat and Durum
IGP Institute Capitalizes on Resources and Location to Provide Hands-on Training
Wheat Foods Council Is A Leading Source Of Science-Based Wheat Foods Information