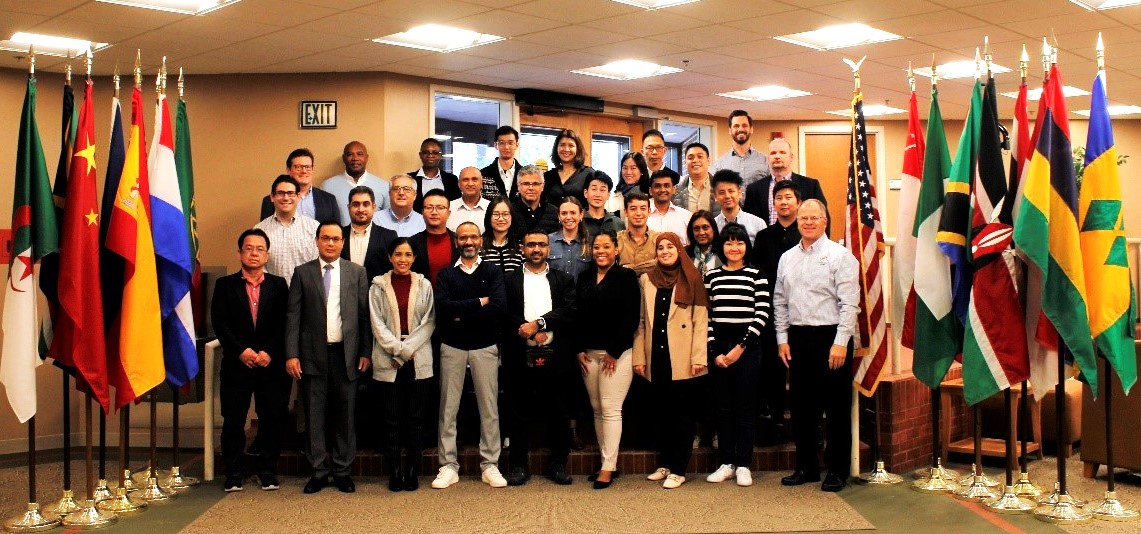
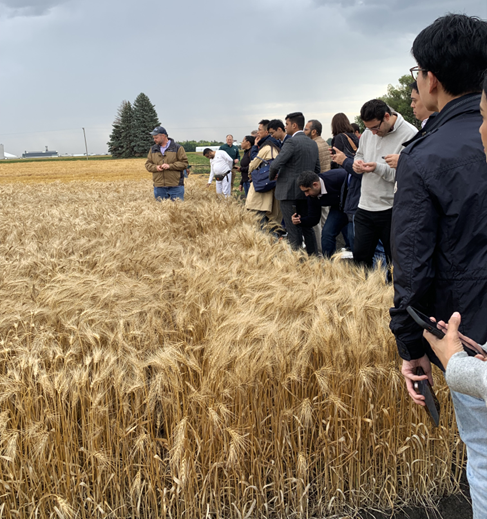
Flour milling companies from nine European countries made up a delegation that visited Washington, D.C. Sept. 24-28 to learn about the 2023 U.S. wheat crop and developments involving global markets, trade policy and emerging technologies.
U.S. Wheat Associates (USW) hosted the team, providing a series of presentations by USW staff and representatives of partner organizations.

USW’s Ian Flagg, right, greets members of the European flour millers delegation and USW partner organizations during meetings in Washington, D.C.
Sharing Information
“Our efforts to increase U.S. wheat market share in Europe includes sharing information to major and larger mid-size mills and traders, many who are interested in hard red spring (HRS) and durum wheat,” said Ian Flagg, USW Regional Vice President for European, Middle Eastern and North African Regions. “Strategically, it’s important to work with agencies, milling associations and traders and discuss issues that are limiting European market access. At the same time, it’s a chance to talk about U.S. wheat and remind them about the advantages it offers milling companies and end-users.”
Italy, France, Germany, Poland, Slovenia, Lithuania, the United Kingdom, Ireland, and Belgium were represented on the delegation. The visit is an initiative of the European Flour Millers Association that involves exploring different markets each year.
U.S. Durum, HRS Customers
Flagg welcomed its members to Washington and gave a broad overview of the U.S. wheat industry. About 70% of U.S. durum exports go to the EU, with Italy taking a large portion of that for pasta production, Flagg noted, adding that European countries import HRS from the U.S. mostly to blend with other wheat.
USW’s data shows that U.S. market share in the EU tends to vary from year to year, and in the past few years has swung from 17% to 33% for high protein milling wheat (mostly HRS) and from 18% to 28% for durum.
Crop Quality, Trade Policy Updates
Jim Peterson, Policy and Marketing Director for the North Dakota Wheat Commission, gave the delegation a U.S. wheat crop quality update. Other presenters included Ryan Caffery of CHS, who offered insights into both the opportunities and constraints involving the European market.
USW Vice President of Trade Policy Dalton Henry spoke about technology and government actions that affect wheat trade.
“It was great to talk with this group because, from a policy standpoint, there are many areas where we work together – namely on food safety and production technologies,” said Henry. “Having dialogue on those topics is critical, especially as new technologies come to market or regulations are being drafted as it gives us the best chance to prevent trade disruptions in the future.”

Representatives of flour millers from nine European countries pose for a group photo during its visit to Washington, D.C.
Team Effort
USDA, the North American Export Grain Association (NAEGA), the National Grain and Feed Association (NGFA) and the North American Millers’ Association (NAMA) each participated by in sharing related information about opportunities and issues they face.

USW Vice President of Trade Policy Dalton Henry spoke about technology and government actions that affect wheat trade.
Along with Canada, competitors for U.S. HRS are high-protein Russian and Kazakh spring wheat, though export volumes are relatively small. Ukraine is another large supplier of wheat to the EU but is not considered a competitor for HRS due to its low and medium quality. Competitors for U.S. durum wheat are Canada, Russian, Kazakh, Australian and Mexico.
Tour of Facilities
Aside from meetings and presentations, USW offered the EU team a look at some U.S. milling facilities and a wholesale bakery. It toured Miller Milling in Westchester, Virginia, which produces a variety of durum and hard wheat products. It also services an adjacent pasta manufacturing facility. The visit to Uptown Bakers featured a look at its 40,000 square foot facility just outside of D.C. Uptown has more than 500 restaurants, hotels, and caterers as clients.
The team was also able to explore Chesapeake Farms, which is owned by Corteva Agriscience. The 3,300 acres of Chesapeake Farms are devoted to the development, evaluation, and demonstration of advanced agricultural practices.